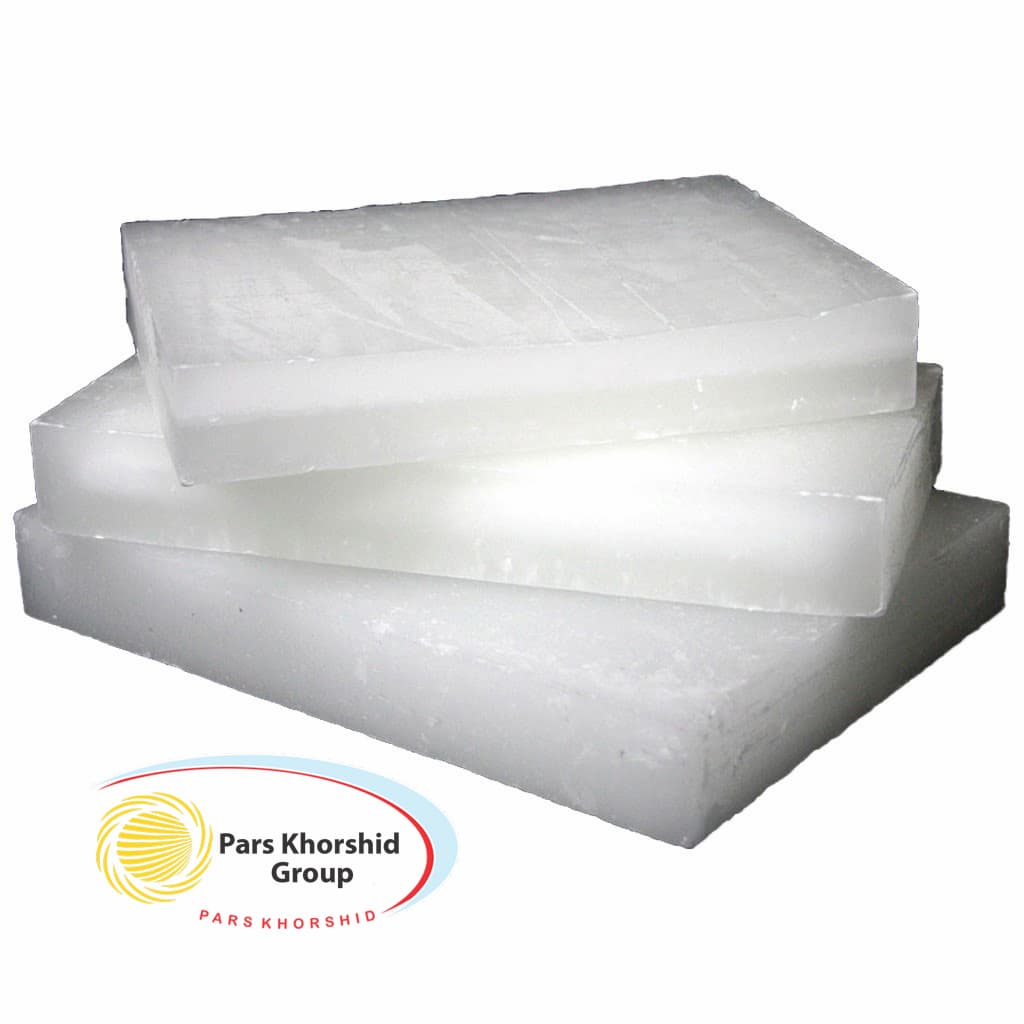

Paraffin Wax is one form of wax that has a colorless white appearance; It is a tasteless and odorless solid material that is produced by the refining of crude oil. It is a heavy, saturated, aliphatic oil, the carbon number of which falls typically in the range of twenty to forty carbons. Covalent bonds in the material demonstrated features such as low melting point, and high thermal stability and it is a good water-repellent; it has numerous uses.
Paraffin Wax is an invaluable material in various fields due to its physical and chemical characteristics. Some of the key benefits and properties of this material include:
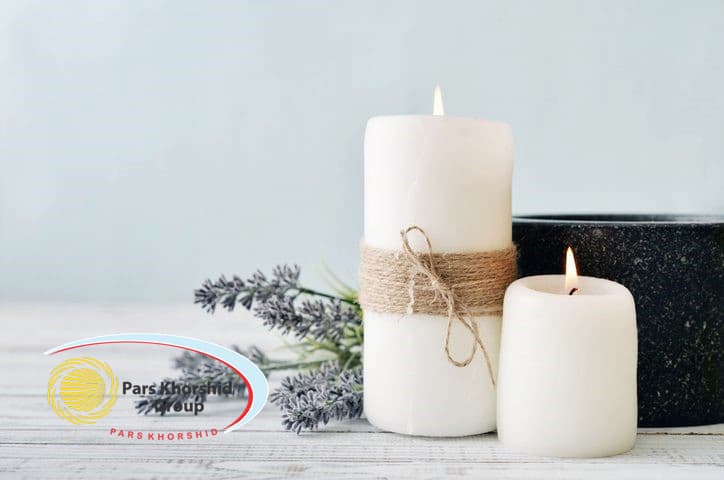

The choice of the grade and type of Paraffin Wax will depend on the use of the wax and the desired characteristics. Some of the common grades and types of this material include:
Type | Usage | Characteristics |
Food-Grade | Food Packaging and Processing | Stringent Purity and Safety Standards |
Cosmetic-Grade | Cosmetic and Personal Care Products | Highly Purified and Meets Specific Regulatory Requirements |
Industrial-Grade | Wide Range of Industrial Applications, Such As Coatings, Sealants, and Lubricants | Low Reactivity, Excellent Electrical Insulating Properties |
Microcrystalline | Candles, Coatings, and Specialty Applications | Finer Crystalline Structure |
Fully Refined | Food Industry, Making Candles and Sculpture Art | Extensive Refining and Purification, Higher Degree of Purity and Clarity |
Slack Wax | By-product of The Dewaxing Process | Contains A Higher Percentage of Oil Compared to Fully Refined paraffin wax |
Paraffin Wax can be obtained through the distillation and refining process of crude oil. The process involves the following steps:
Due to its unique characteristics and versatility, Paraffin Wax can meet different requirements and functions in many fields, and the use of this material is extensive in different industries. Some of the key applications include:

In addition to its industrial applications, Paraffin Wax has also found its way into the world of skincare and beauty treatments. It is known for its ability to deeply hydrate and condition the skin, making it a popular ingredient in various skincare and beauty products, such as Paraffin Wax Baths, Paraffin Wax Masks and Treatments, Paraffin Wax Candles and Melts, and Paraffin Wax in Makeup and Cosmetics.
While Paraffin Wax is generally considered a safe material, it is important to take certain precautions when handling and using it. Some key safety considerations include:
While Paraffin Wax is a versatile and widely-used material, there are also alternative uses and substitutes available, depending on the specific application and requirements. The choice of alternative or substitute material will depend on the specific requirements of the application, as well as factors such as cost, availability, and regulatory compliance. Some examples include:
While Paraffin Wax is generally considered a safe and environmentally friendly material, proper disposal and containment of paraffin wax waste are important to minimize any potential environmental impact. Some concerns may arise from the use of petroleum-based raw materials in the production of paraffin wax.